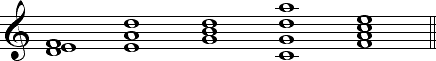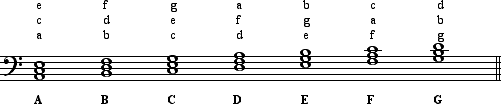
 |
|
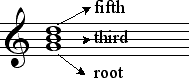
IntroductionAs we have already learned, two pitches sounding simultaneously is a harmonic interval. Three or more pitches sounding simultaneously is a chord. Although chords can be built by stacking intervals of any size, those built in thirds are the most common. Following are examples of various chords: 1TriadsMost of the harmony we encounter in Western culture is based on triads. This is called tertian harmony and was standard from about 1600 to 1900. A triad is a three-note chord built in thirds. Examples of all the triads built on the white keys of the piano are shown below: Every triad consists of three components: a root, a third, and a fifth. The root is the tone from which the chord is both constructed and named. The following chord, therefore, is a G chord.
|